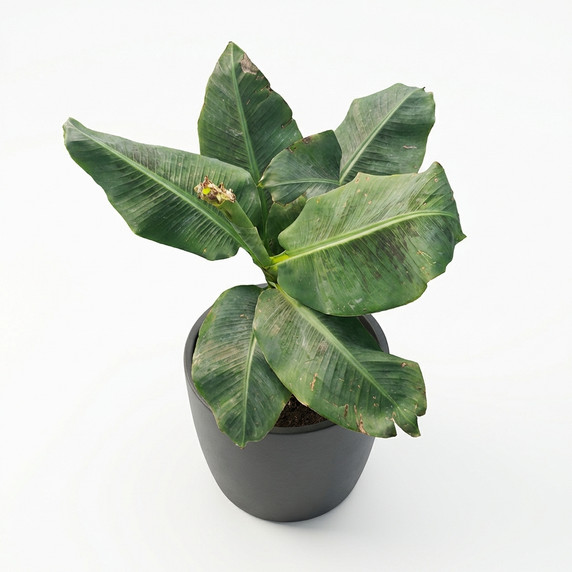
Musaceae
Musa × paradisiaca
Bring the tropics home with the Banana Plant—lush, oversized leaves that transform any corner into a green getaway. Perfect as a floor statement plant for bright interiors and patios, it grows quickly and looks fuller with each new leaf. With regular watering, warmth, and a little feeding, Musa rewards you with dramatic, architectural greenery that elevates living rooms, receptions, and modern commercial spaces.
1. Basic Identification
Plant Science Name: Musa × paradisiaca
Plant Varient: Standard
Plant Color: Natural
Plant Country: Not mentioned
SKU: PLT-0089
Arabic Name: موز
Stems:
Family: Musaceae
2. Taxonomy & Classification
Order: Zingiberales
Family: Musaceae
Genus: Musa
Section: Musa sect. Musa
3. Origin & Distribution
Native to Southeast Asia (Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines). Widely cultivated and naturalized throughout tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, including Africa, Central and South America, the Caribbean, and India.
4. Visual Characteristics
Forms an upright pseudostem composed of tightly rolled leaf sheaths. Leaves are large, elongated, bright to deep green, up to 2.5 m long and 60 cm wide, with a prominent midrib. When mature, the plant produces hanging clusters of curved, elongated fruits (bananas) that turn yellow when ripe.
5. Size & Dimensions
Height: 2–8 m outdoors; typically 1.5–3 m when grown in containers indoors.
Spread: 1–5 m depending on growing space.
Leaf Length: 1–3 m; leaf width up to 60 cm.
6. Light Requirements
Thrives in full sun to partial shade. Indoors, place in bright, indirect light near a south- or west-facing window. Tolerates some direct morning or late afternoon sun; avoid intense midday sun on young leaves.
7. Watering Needs
Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Water thoroughly when the top 2–3 cm of soil begins to dry. Increase frequency during warm, active growth; reduce slightly in cooler months.
8. Soil & Potting
Prefers a rich, well-draining loam or potting mix amended with generous organic matter (compost or well-rotted manure). Ideal pH is 5.5–7.0. Ensure good drainage to prevent root rot; use pots with multiple drainage holes.
9. Temperature & Humidity
Optimal temperature range is 24–30 °C; avoid temperatures below 15 °C. Requires high humidity (50–70%+). Increase humidity with regular misting, humidifiers, or placing the pot on a pebble tray with water.
10. Fertilization
Heavy feeder: apply a balanced N-P-K fertilizer (e.g., 10-10-10) monthly during the growing season. Alternatively, use a high-potassium fertilizer every 4–6 weeks to support fruiting. Reduce feeding in winter.
11. Maintenance & Care Level
Moderate care level. Needs space for growth, regular watering, feeding, and high humidity. Remove dead or damaged leaves to maintain appearance and prevent pests. Provide support for heavy pseudostems if needed.
12. Growth & Propagation
Propagated primarily by division of suckers (pups) that form at the base of the parent plant. Allow pups to reach 25–30 cm tall before separating. Also propagated by tissue culture in commercial operations.
13. Common Problems
Overwatering can lead to root and pseudostem rot. Leaf spot diseases (e.g., Sigatoka) in humid conditions. Pests include aphids, spider mites, thrips, and mealybugs. Nutrient deficiencies (especially potassium) cause yellowing or brown leaf edges.
14. Benefits & Uses
Produces edible fruit widely consumed fresh or processed. Young leaves and shoots are used as food or wrapping material. Pseudostem fiber can be used for textiles and paper. Popular ornamental specimen for tropical-themed landscapes and large interiors.
15. Toxicity & Safety
Non-toxic to humans and pets. All parts are considered safe; fruits are a nutritious food source. Large, fallen leaves can create slip hazards if left on paths.

Musa × paradisiaca
Bring the tropics home with the Banana Plant—lush, oversized leaves that transform any corner into a green getaway. Perfect as a floor statement plant for bright interiors and patios, it grows quickly and looks fuller with each new leaf. With regular watering, warmth, and a little feeding, Musa rewards you with dramatic, architectural greenery that elevates living rooms, receptions, and modern commercial spaces.
1. Basic Identification
Plant Science Name: Musa × paradisiaca
Plant Varient: Standard
Plant Color: Natural
Plant Country: Not mentioned
SKU: PLT-0089
Arabic Name: موز
Stems:
Family: Musaceae
2. Taxonomy & Classification
Order: Zingiberales
Family: Musaceae
Genus: Musa
Section: Musa sect. Musa
3. Origin & Distribution
Native to Southeast Asia (Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines). Widely cultivated and naturalized throughout tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, including Africa, Central and South America, the Caribbean, and India.
4. Visual Characteristics
Forms an upright pseudostem composed of tightly rolled leaf sheaths. Leaves are large, elongated, bright to deep green, up to 2.5 m long and 60 cm wide, with a prominent midrib. When mature, the plant produces hanging clusters of curved, elongated fruits (bananas) that turn yellow when ripe.
5. Size & Dimensions
Height: 2–8 m outdoors; typically 1.5–3 m when grown in containers indoors.
Spread: 1–5 m depending on growing space.
Leaf Length: 1–3 m; leaf width up to 60 cm.
6. Light Requirements
Thrives in full sun to partial shade. Indoors, place in bright, indirect light near a south- or west-facing window. Tolerates some direct morning or late afternoon sun; avoid intense midday sun on young leaves.
7. Watering Needs
Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Water thoroughly when the top 2–3 cm of soil begins to dry. Increase frequency during warm, active growth; reduce slightly in cooler months.
8. Soil & Potting
Prefers a rich, well-draining loam or potting mix amended with generous organic matter (compost or well-rotted manure). Ideal pH is 5.5–7.0. Ensure good drainage to prevent root rot; use pots with multiple drainage holes.
9. Temperature & Humidity
Optimal temperature range is 24–30 °C; avoid temperatures below 15 °C. Requires high humidity (50–70%+). Increase humidity with regular misting, humidifiers, or placing the pot on a pebble tray with water.
10. Fertilization
Heavy feeder: apply a balanced N-P-K fertilizer (e.g., 10-10-10) monthly during the growing season. Alternatively, use a high-potassium fertilizer every 4–6 weeks to support fruiting. Reduce feeding in winter.
11. Maintenance & Care Level
Moderate care level. Needs space for growth, regular watering, feeding, and high humidity. Remove dead or damaged leaves to maintain appearance and prevent pests. Provide support for heavy pseudostems if needed.
12. Growth & Propagation
Propagated primarily by division of suckers (pups) that form at the base of the parent plant. Allow pups to reach 25–30 cm tall before separating. Also propagated by tissue culture in commercial operations.
13. Common Problems
Overwatering can lead to root and pseudostem rot. Leaf spot diseases (e.g., Sigatoka) in humid conditions. Pests include aphids, spider mites, thrips, and mealybugs. Nutrient deficiencies (especially potassium) cause yellowing or brown leaf edges.
14. Benefits & Uses
Produces edible fruit widely consumed fresh or processed. Young leaves and shoots are used as food or wrapping material. Pseudostem fiber can be used for textiles and paper. Popular ornamental specimen for tropical-themed landscapes and large interiors.
15. Toxicity & Safety
Non-toxic to humans and pets. All parts are considered safe; fruits are a nutritious food source. Large, fallen leaves can create slip hazards if left on paths.