Lamiaceae
Salvia rosmarinus
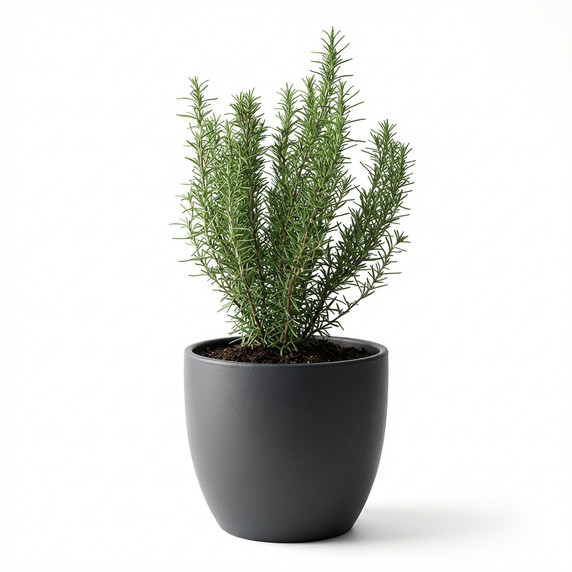
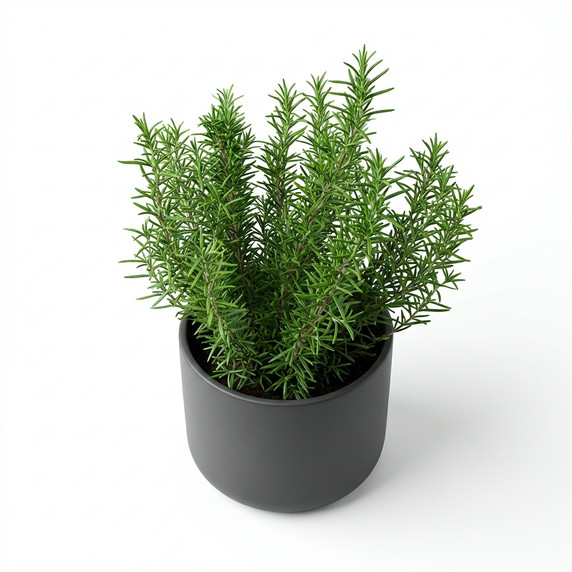
Bring home the scent of the Mediterranean. This potted Rosemary is a hardy, sun-loving herb that looks great on balconies and provides fresh sprigs on demand for roasted meats, potatoes, and teas. With well-draining soil and sensible watering, it stays dense, green, and beautifully fragrant—an ideal edible gift and a staple for any home garden.
1. Basic Identification
Common Name: Rosemary
Botanical Name: Salvia rosmarinus
Former Name: Rosmarinus officinalis
Plant Type: Herbaceous perennial subshrub
Plant Code / SKU: PLT-0133
Alternative Names:
اكليل الجبل
Common rosemary
Garden rosemary
Polar plant
Waxy-leaved rosemary
2. Taxonomy & Classification
Order: Lamiales
Family: Lamiaceae
Genus: Salvia
Species: Salvia rosmarinus (syn. Rosmarinus officinalis)
3. Origin & Distribution
Native to the Mediterranean region, including southern Europe (Italy, Spain), northern Africa, and western Asia. Widely cultivated and naturalized in temperate regions around the world as a culinary and ornamental herb.
4. Visual Characteristics
Evergreen perennial with woody stems; leaves are linear-needle, 2–4 cm long, dark green on top with silvery-white undersides. Flowers are tubular, pale blue to violet (occasionally white), appearing in clusters along the stems from spring through summer.
5. Size & Dimensions
Height: 50–100 cm
Width (Spread): 50–100 cm
Growth Rate: Moderate (15–30 cm per year)
6. Light Requirements
Full sun (minimum 6–8 hours of direct sunlight daily). Tolerates light shade but may become leggy and lose aromatic potency if light is insufficient.
7. Watering Needs
Moderate watering. Allow the top 2–3 cm of soil to dry between waterings. Drought tolerant once established. Avoid waterlogged soil to prevent root rot. Reduce frequency in winter.
8. Soil & Potting
Prefers a well-draining, sandy or loamy soil mix with pH 6.0–7.5. In containers, use a gritty potting mix amended with perlite or coarse sand. Ensure pots have adequate drainage holes. Repot every 2–3 years in spring.
9. Temperature & Humidity
Optimal daytime temperatures: 15–24 °C. Tolerates down to –10 °C when established outdoors; best kept above 4 °C in containers. Prefers low to average humidity and good air circulation to reduce fungal diseases.
10. Fertilization
Light feeder. Apply a balanced fertilizer (e.g., 10-10-10 NPK) diluted to half strength once a month during the growing season (spring–summer). Avoid excessive nitrogen to prevent overly lush, weak growth. No feeding in winter.
11. Maintenance & Care Level
Low to moderate care. Prune lightly after flowering to maintain shape and promote bushiness. Remove dead or woody stems annually. Pinch new growth tips to encourage dense foliage.
12. Growth & Propagation
Propagate by semi-hardwood cuttings in summer: take 8–10 cm cuttings, strip lower leaves, root in a sandy or perlite mix at 20–24 °C; roots form in 3–6 weeks. Can also be grown from seed, by layering, or by division.
13. Common Problems
Pests: Aphids, spider mites, whiteflies, mealybugs.
Diseases: Root rot (from overwatering), powdery mildew.
Prevention/Treatment: Ensure good drainage and air circulation; avoid overhead watering; treat pests with insecticidal soap or neem oil; remove and dispose of affected foliage.
14. Benefits & Uses
Culinary: Flavoring for meats, vegetables, breads, sauces, and teas.
Medicinal: Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, aids digestion, may enhance memory.
Ornamental: Fragrant evergreen foliage and attractive flowers; dried for arrangements.
Aromatherapy & Cosmetics: Essential oil used in diffusers, soaps, and lotions.
15. Toxicity & Safety
Generally non-toxic to humans and pets when used in culinary amounts. Concentrated essential oils can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions; may be contraindicated in pregnancy and for individuals with epilepsy. Avoid contact with eyes and mucous membranes.

Salvia rosmarinus
Bring home the scent of the Mediterranean. This potted Rosemary is a hardy, sun-loving herb that looks great on balconies and provides fresh sprigs on demand for roasted meats, potatoes, and teas. With well-draining soil and sensible watering, it stays dense, green, and beautifully fragrant—an ideal edible gift and a staple for any home garden.
1. Basic Identification
Common Name: Rosemary
Botanical Name: Salvia rosmarinus
Former Name: Rosmarinus officinalis
Plant Type: Herbaceous perennial subshrub
Plant Code / SKU: PLT-0133
Alternative Names:
اكليل الجبل
Common rosemary
Garden rosemary
Polar plant
Waxy-leaved rosemary
2. Taxonomy & Classification
Order: Lamiales
Family: Lamiaceae
Genus: Salvia
Species: Salvia rosmarinus (syn. Rosmarinus officinalis)
3. Origin & Distribution
Native to the Mediterranean region, including southern Europe (Italy, Spain), northern Africa, and western Asia. Widely cultivated and naturalized in temperate regions around the world as a culinary and ornamental herb.
4. Visual Characteristics
Evergreen perennial with woody stems; leaves are linear-needle, 2–4 cm long, dark green on top with silvery-white undersides. Flowers are tubular, pale blue to violet (occasionally white), appearing in clusters along the stems from spring through summer.
5. Size & Dimensions
Height: 50–100 cm
Width (Spread): 50–100 cm
Growth Rate: Moderate (15–30 cm per year)
6. Light Requirements
Full sun (minimum 6–8 hours of direct sunlight daily). Tolerates light shade but may become leggy and lose aromatic potency if light is insufficient.
7. Watering Needs
Moderate watering. Allow the top 2–3 cm of soil to dry between waterings. Drought tolerant once established. Avoid waterlogged soil to prevent root rot. Reduce frequency in winter.
8. Soil & Potting
Prefers a well-draining, sandy or loamy soil mix with pH 6.0–7.5. In containers, use a gritty potting mix amended with perlite or coarse sand. Ensure pots have adequate drainage holes. Repot every 2–3 years in spring.
9. Temperature & Humidity
Optimal daytime temperatures: 15–24 °C. Tolerates down to –10 °C when established outdoors; best kept above 4 °C in containers. Prefers low to average humidity and good air circulation to reduce fungal diseases.
10. Fertilization
Light feeder. Apply a balanced fertilizer (e.g., 10-10-10 NPK) diluted to half strength once a month during the growing season (spring–summer). Avoid excessive nitrogen to prevent overly lush, weak growth. No feeding in winter.
11. Maintenance & Care Level
Low to moderate care. Prune lightly after flowering to maintain shape and promote bushiness. Remove dead or woody stems annually. Pinch new growth tips to encourage dense foliage.
12. Growth & Propagation
Propagate by semi-hardwood cuttings in summer: take 8–10 cm cuttings, strip lower leaves, root in a sandy or perlite mix at 20–24 °C; roots form in 3–6 weeks. Can also be grown from seed, by layering, or by division.
13. Common Problems
Pests: Aphids, spider mites, whiteflies, mealybugs.
Diseases: Root rot (from overwatering), powdery mildew.
Prevention/Treatment: Ensure good drainage and air circulation; avoid overhead watering; treat pests with insecticidal soap or neem oil; remove and dispose of affected foliage.
14. Benefits & Uses
Culinary: Flavoring for meats, vegetables, breads, sauces, and teas.
Medicinal: Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, aids digestion, may enhance memory.
Ornamental: Fragrant evergreen foliage and attractive flowers; dried for arrangements.
Aromatherapy & Cosmetics: Essential oil used in diffusers, soaps, and lotions.
15. Toxicity & Safety
Generally non-toxic to humans and pets when used in culinary amounts. Concentrated essential oils can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions; may be contraindicated in pregnancy and for individuals with epilepsy. Avoid contact with eyes and mucous membranes.